- Phone: +91 9022447976 | +91 9106194096
- 24x7 Hours Working Hospital
- info@urbanhealhospital.com | drkartik@urbanhealhospital.com

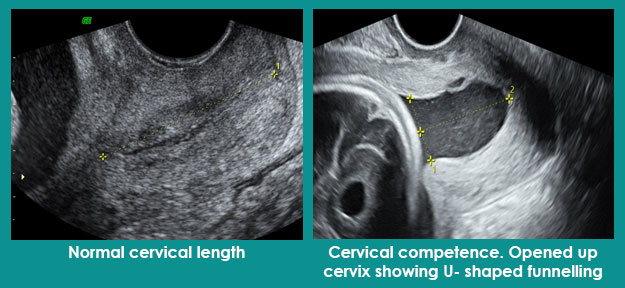
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (mouth of the uterus). It is this that shortens and opens up allowing the passage of baby during the childbirth. We want it to remain long and closed throughout the pregnancy and open up only at the time of childbirth.
Measuring the length of the cervix is called as cervical length screening.
The purpose is to determine whether the cervix is short or long and whether it has started opening (called as funnelling) up or not. Any cervical length which is < 25 mm is labelled as short cervix.
Pregnancies with short cervices are at increased risk of second trimester miscarriage or delivery before 34 weeks.
It is always done vaginally. We can do it from abdomen as well, however, that assessment for length is spurious.
There is no specific time period. We do cervical length measurement transvaginally at the time of first trimester screening as it provides us a baseline. Then depending on women’s previous history of preterm delivery or second trimester miscarriage or clinical complaints like pain or heaviness in the lower abdomen, bleeding or leakage of fluid per vaginum, we do an internal scan for cervical length assessment.
We follow the protocol as laid down by Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF), UK.
This is the most common question we are asked. Transvaginal ultrasound is absolutely safe. It will not harm the baby or induce miscarriage or bleeding. At the most, you might feel a slight discomfort while undergoing transvaginal scan but then this also depends on your pain threshold.
Amniocentesis is a test offered in the second trimester of pregnancy. A small sample of fluid is taken from the amniotic sac using the needle. The amniotic sac is the sac which contains the baby and the fluid around it inside the uterus. This fluid around the baby has baby’s shed cells. These cells are extracted and used to check if there is a chromosomal or any other genetic problem in the baby.
Amniocentesis is offered
a. If prenatal screening shows there is an increased chance of a chromosomal problem like Down syndrome,Getting the test done is completely your choice. We can suggest what is good practice based on evidence-based medicine. Knowing all the pros and cons, you can accept or decline the testing.
It is usually done after 15 completed weeks. It can be done uptil any time, however, in the third trimester the number of cells in the fluid decreases, so might not be able to give any result. We usually do it between 16 to 20-24 weeks. The MTP act allows termination till 20 weeks, hence we prefer, it to be done earlier than 20 weeks.
There is minimal risk of miscarriage about 1: 1000. We do not know why it happens or to whom it will happen. It does not cause any birth defects or any harm to the mother. The risk of infection is also very low, 1 in 1000.
You are made to rest for half an hour after the procedure. The fetal heart beat is checked and then you are sent home. Most women have no problems, but you might have a bruise, spotting or cramping. If you do, paracetamol is safe to take. If you have a persistent pain, leaking, bleeding or a high temperature, then you need to go to the hospital.
You can consult with Dr. Neha Gupta. She is one of the best fetal medicine specialists and is experienced in handling lots of pregnant women to take care of their unborn baby. Contact us to get the appointment and discuss it with her.
An Intrauterine transfusion (IUT) is a procedure in which blood is transfused into a fetus, most commonly through the umbilical cord. It is used in cases of severe fetal anaemia.
Fetal anaemia occurs in haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
For HDFN to occur, the fetus must have a positive blood group (paternally inherited) and the mother must have negative blood group. Fetal red cells has the Rh factor which is the antigen which the mother does not have. When mother is exposed to the Rh factor during a previous pregnancy or transfusion, mother develops antibodies to the Rh factor.
In the next pregnancy, maternal antibodies cross the placenta during pregnancy and destroy fetal red blood cells (RBCs). This process can lead to fetal anaemia, and in severe cases can progress to hydrops (edema), ascites, heart failure, and death.
However, the rates of these cases have significantly reduced by Anti-D immunoglobulin administration.
Fetal anaemia is monitored throughout pregnancy using Doppler measurement of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) peak systolic velocity (PSV). Once MCA-PSV value exceeds 1.5 MoM, it indicates development of fetal anaemia. At this point, invasive testing via percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling (PUBS, also called cordocentesis) is done followed by fetal transfusion
Prior to the procedure, the compatible blood is obtained. O, RhD-negative, and antigen-negative for maternal RBC antibodies is selected. The selected blood then undergoes irradiation and leukocyte reduction. Antenatal corticosteroids are typically given to mothers before IUT to anticipate the need for an emergency caesarean section.
The procedure is usually performed in a hospital under sterile conditions. The mother’s abdomen is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. She is given a local anaesthetic injection to numb the abdominal area from where the transfusion needle will be inserted. During the procedure, medicine is given to the fetus in its thigh to temporarily stop the fetal movements.
An ultrasound is performed to view the position of the fetus and to help guide the needle. The first step is to locate a relatively stable segment of the umbilical cord. Once a suitable location is established, the needle is inserted through the mother’s abdomen into an umbilical vessel using ultrasound guidance. If insertion into an umbilical vessel is not possible, blood may be transfused into the portion of the umbilical vein in the fetal abdomen.
Prior to the transfusion, percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling (PUBS) is conducted. The fetal blood sample is drawn and immediately analysed for haematocrit in the hospital haematology laboratory. The result confirms the level of fetal anaemia and indicates the correct amount of blood to be transfused. With the needle still in place, the blood is delivered into the fetus’s umbilical cord blood vessel. Following the transfusion, an additional blood sample is drawn and analysed to determine the final hemoglobin.
Fetal survival rates after intrauterine transfusion through the umbilical cord are more than 90% for fetuses that do not have hydrops and about 75% for fetuses that have hydrops
Risks of intrauterine transfusions may include uterine infection, fetal infection, preterm labour, excessive bleeding and mixing of fetal and maternal blood, amniotic fluid leakage from the uterus, slowing of fetal hearty rate, bleeding from the umbilical cord puncture site or (rarely) fetal death. There is only 1-2% risk of such complications.
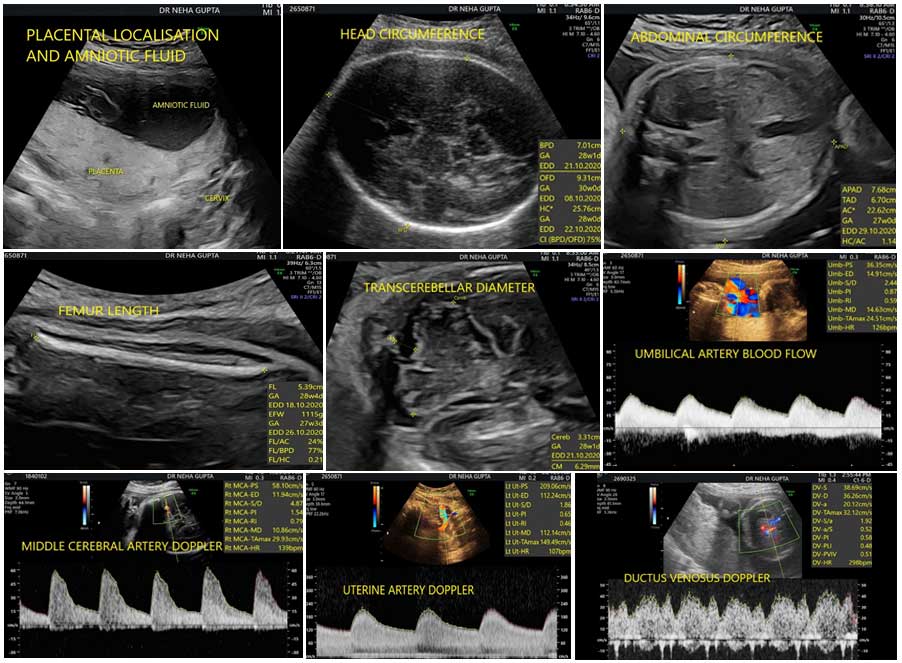
This scan is meant to assess the fetal weight, the fluid around the baby, the placental localisation and the blood flows to the baby.
Fetal dopplers mean assessment of baby’s blood flows. Maternal blood flows to the uterus are assessed by uterine artery Dopplers. Blood flow through cord is called as umbilical artery blood flow. Blood through baby’s brain is called as middle cerebral artery Dopplers and through tummy is referred to as ductus venosus Dopplers.
The aim is to assess the fetal growth disorders and the well being of the unborn baby. If the growth is appropriate for the weeks, then it is normal. If the growth is small, then it is a weak baby, also called as fetal growth restriction. If the growth is high, then it is a big baby, also called as macrosomia.
Besides fetal weight, maternal history and symptoms, fluid assessment and baby’s blood flows helps us to further identify the babies at risk of adverse outcome. Depending on the above factors, appropriately delivery can be timed.
No, minimum two growth scans are required to assess the fetal well being. One growth scan gives us the fetal growth assessment at a given time. However, two helps us to establish the growth velocity, and identify the at risk fetuses.
A detailed structural assessment is difficult after 26-28 weeks due to fetal position and baby does not move around completely as it does around 20 weeks. But still, whatever is possible due to fetal position and advanced gestational age, is assessed at the time of growth scans.
Yes, it is possible. The risk of detection of structural abnormality in the third trimester is 1 in 200 pregnancies. These could be those that develop later on like certain brain abnormalities, kidney problems or those which were missed at the time of anomaly scan.
Usually, the growth and Doppler assessment start from 28 weeks onwards. Most of the times, two scans are done for the growth assessment- one around 28 weeks and other between 34-37 weeks. Sometimes, depending on the growth and blood flows or specific history, more scans may also be required. This will be explained to you by the fetal medicine specialist.
No. But at this time, if the fetal position is appropriate, good 3D and 4D views can be obtained of the face of the fetus. We routinely take 3D/4D views of the face if the baby’s position is appropriate.
Individuals who routinely perform obstetric scans and have the necessary requirements as per the law of the land.
Prenatal ultrasonography appears to be safe for clinical practice. To date, there has been no independently confirmed study to suggest otherwise.
A multiple pregnancy is one in which the mother carries more than one baby in her womb. Most commonly is it two called as twins. If there are three, it is called as triplet and if four, it is quadruplet pregnancy.
Fertilization of egg by a sperm is called zygote which later develops into embryo and then baby.
In non-identical twins (DIZYGOTIC), each egg is fertilized by different sperm. It is like two/ multiple babies with different genetic material growing in the womb at the same time.
This usually happens two or more eggs ovulate at the same time and get fertilized or two or more embryos were transferred in intro-fertilization process.
Identical twins (MONOZYGOTIC) develop from one egg and one sperm forming one zygote. Very early in the process, the fertilized egg or zygote splits into two or more embryos.
This is the concept of ZYGOSITY.
Monozygotic are the identical twins. They can be
Dizygotic will always be dichorionic and diamniotic- each baby has their own placenta and sacs.
This the concept of CHORIONICITY.
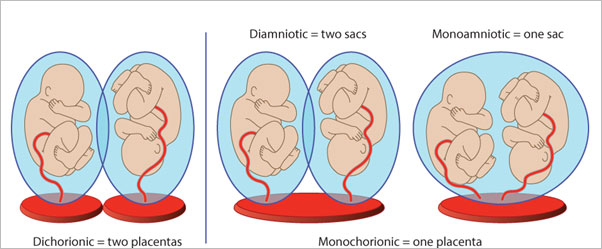
Chorionicity is to determine the type of placentation. Hence, we determine chorionicity and zygosity on the ultrasound.
Determination of chorionicity is important as it determines the type of complications the babies can have and the type of follow up they require.
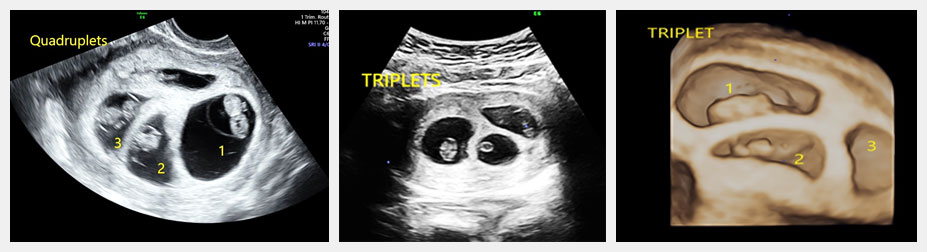
The care has to be individualised for every multiple pregnancy. As these pregnancies are at risk of early delivery, weak babies, developing high blood pressure and sugars, hence the monitoring of babies by ultrasound needs to be individualised.
Also, the monochorionic pregnancies have unique set of complications like twin to twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) where one baby bleedss into the other twin or selective fetal growth restriction, where one baby grows really small in comparison to the other baby. Hence, depending on how each multiple pregnancy behaves, we have to alter the protocol.
I can understand that these are somewhat difficult to understand but if you have any queries, I would be eager to answer all of them.
Genetic counseling is the information provided by the counselor as to how certain genetic disease might affect you and your family and what is the risk of transmission to your children. The doctor will first collect your and family history.
It is done in those cases-
After counseling, a repeat scan or certain tests might be prescribed.
WHAT IS 3D/4D ULTRASOUND?
There are 2D, 3D and 4D ultrasounds. All ultrasound uses sound waves to create an image of the unborn baby on the screen. A 2D ultrasound of a fetus creates a black-and-white image. The main scan is done in 2D only. We take images of the unborn baby in grey scale. We take measurements of the unborn baby, assess its growth and assess the structure of the baby mainly in 2D.Nowadays, 3D- three dimensional and 4D – fourth dimensional ultrasounds have become common. Usually, all ultrasound machines have software and volume probes with which we do 3D/ 4D scan.3D scan makes three dimensional images of the unborn baby like that of a face. When we see these images in real time, that is, we see the movements of the unborn baby as well, it is called 4D ultrasound. Some centres have started adding 5D ultrasound also. 5D ultrasound is nothing but an extension of 3D ultrasound only.
The main scan is done in grey scale, that is 2D scanning. 3D and 4D ultrasounds can be used by the person to add more information to it but are not absolutely necessary.
What laymen understand is that , by means of 3D and 4D ultrasound , the parents can see realistic images of the face of the baby. It adds to great experience in pregnancy. But it is not limited to taking pictures of baby’s faces.
The benefits of 3D and 4D ultrasound are limited. It becomes useful when any structural abnormality is suspected. It helps us to take views of the baby from different angles and provides more depth to our understanding of abnormalities. 3D and 4D ultrasounds can be done to add more details which helps us in counselling couples. Like when we see a gap in the lips- cleft lip, 3d and 4D ultrasound helps to know the extent of the gap, whether there is involvement of palate also.
3D and 4D ultrasounds are not generally part of daily prenatal tests. What is interesting is that 3D ultrasounds provide the three-dimensional image of your infant, while 4D ultrasounds provide a live visual effect, such as a clip, you can see your baby smile or yawn.
WhatsApp us